What is Mental Health?
Definition and Importance of Mental Health
Mental health encompasses our emotional, psychological, and social well-being. It affects how we think, feel, and act and is vital at every stage of life, from childhood and adolescence through adulthood. Understanding Mental health is crucial, as it influences our relationships, decision-making, and overall quality of life.
Good mental health is more than just the absence of mental illness; it represents a state of well-being where individuals can cope with the normal stresses of life, work productively, and contribute to their communities. It involves balancing emotional health, social relationships, and daily functioning.
Common Misconceptions about Mental Health
Despite its importance, mental health is often misunderstood. Here are some common misconceptions:
- Mental health issues are uncommon: Many individuals struggle with mental health problems, making them more common than most people think.
- Only certain demographics are affected: Mental health issues can affect anybody, regardless of age, gender, or background.
- Mental health conditions are not real illnesses: Mental health issues are legitimate medical conditions, similar to physical health conditions.
- People with mental health problems are dangerous: This stereotype is often perpetuated by media portrayals and does not reflect the reality that most individuals with mental health issues are non-violent.
Mental Health vs. Mental Illness
It’s important to differentiate between mental health and mental illness. Mental health refers to the well-being of an individual, while mental illness refers to diagnosable conditions that disrupt this well-being. Mental health can exist on a spectrum, where individuals can experience varying degrees of mental wellness, inconsistently affected by stressors, life changes, and external factors. Mental illnesses, on the other hand, require clinical diagnosis and treatment.
Signs and Symptoms of Mental Health Issues
Understanding Early Warning Signs
Recognizing the early warning signs of mental health issues can significantly impact the approach to treatment and recovery. Common symptoms may include:
- Persistent sadness or low mood
- Changes in appetite or weight
- Withdrawal from social interactions
- Increased sensitivity or emotional swings
- Difficulty concentrating or making decisions
- Feelings of hopelessness or worthlessness
Common Mental Health Conditions
Some of the most common mental health conditions include:
- Anxiety Disorders: Characterized by overwhelming fear or worry.
- Depressive Disorders: Involves persistent feelings of sadness and loss of interest in activities.
- Bipolar Disorder: Marked by extreme mood swings, including emotional highs and lows.
- Schizophrenia: A severe mental disorder affecting how a person thinks, feels, and behaves.
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD): Involves unwanted recurring thoughts and behaviors.
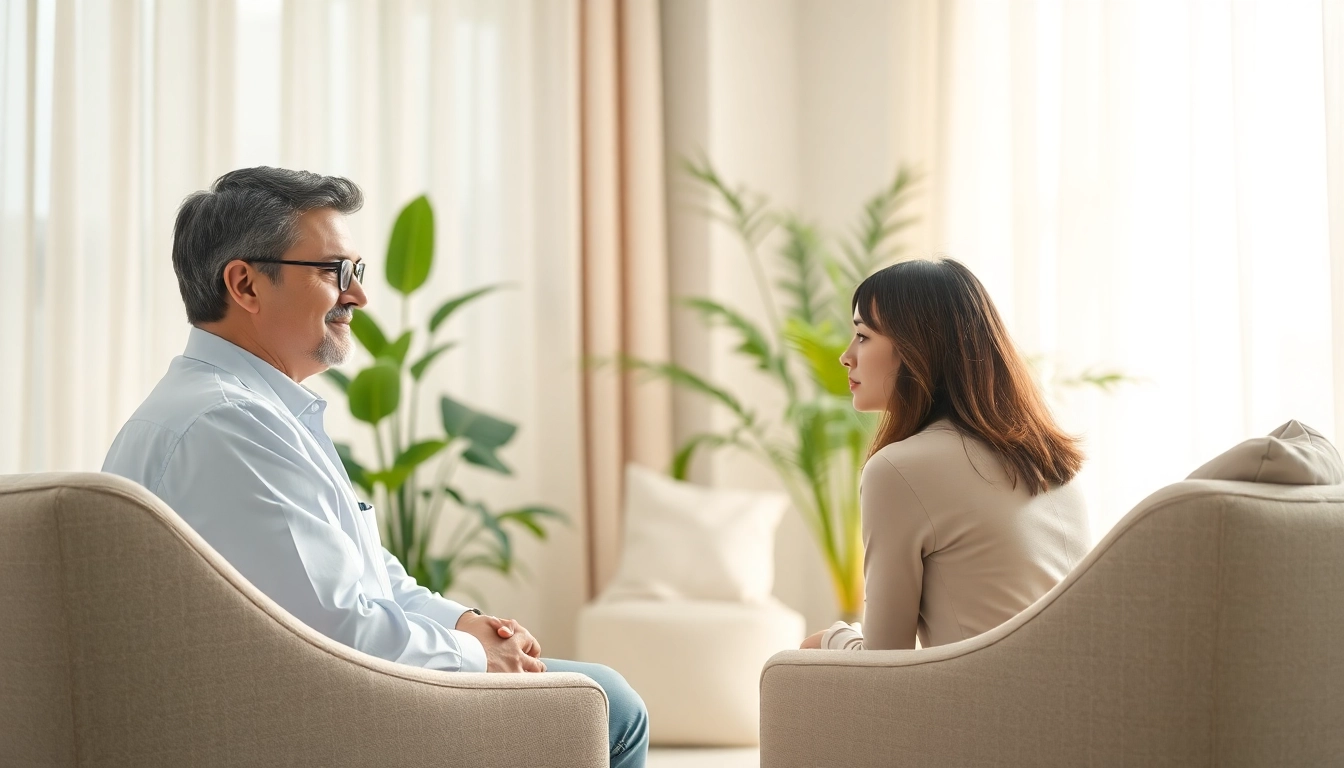
When to Seek Professional Help
Seeking professional help should not be stigmatized. It is essential for individuals who experience persistent symptoms that interfere with daily living, relationships, or work performance. Warning signs that it’s time to seek help include:
- Inactive coping mechanisms, such as substance abuse or self-harm
- Declining performance in work or academic settings
- Feeling unable to cope with daily responsibilities
- Having thoughts of self-harm or harming others
Factors Affecting Mental Health
Environmental Influences on Mental Health
Environmental factors play a significant role in shaping an individual’s mental health. These can include:
- Chronic Stress: Prolonged exposure to stress, whether from work, home, or social situations, can contribute to mental health deterioration.
- Social Isolation: Lack of social support and strong relationships can increase vulnerability to mental health issues.
- Trauma: Experiencing trauma or significant life changes can have long-term effects on mental health.
- Socioeconomic Status: Economic hardships can lead to chronic stress and impact mental wellness.
The Role of Genetics in Mental Health
Genetics can play an influential role in the development of mental health conditions. While not deterministic, family history can increase the risk of various mental illnesses. Research shows that certain conditions, such as depression and bipolar disorder, tend to run in families, indicating that genetic predisposition may affect the likelihood of developing these conditions.
Impact of Lifestyle Choices on Mental Health
Your lifestyle choices significantly influence your mental health. Factors include:
- Diet: A balanced diet can affect mood and energy levels, impacting overall mental wellness.
- Sleep: Quality sleep is crucial for cognitive functions, emotion regulation, and stress management.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise is known to elevate mood and serve as a natural mood enhancer through endorphin release.
- Avoiding Substance Abuse: Alcohol and drugs can exacerbate or lead to mental health issues.
Strategies for Improving Mental Health
Effective Coping Mechanisms
Coping mechanisms are essential for handling stress and maintaining mental health. Effective strategies include:
- Problem-Solving: Identifying problems and brainstorming practical solutions can provide a sense of control.
- Relaxation Techniques: Incorporating techniques such as deep-breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga can reduce stress levels.
- Social Engagement: Connecting with others can provide emotional support and alleviate feelings of isolation.
- Time Management: Developing a structured approach to manage time can reduce overwhelm, enhancing overall productivity.
The Importance of Mindfulness and Therapy
Mindfulness and therapy have been proven effective in promoting mental health. Practices include:
- Mindfulness Meditation: Practicing mindfulness can lead to greater emotional regulation and reduced stress.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT can help in re-framing negative thoughts and developing positive coping strategies.
- Individual or Group Therapy: Talking to a professional or participating in group therapy can provide strategies and support.
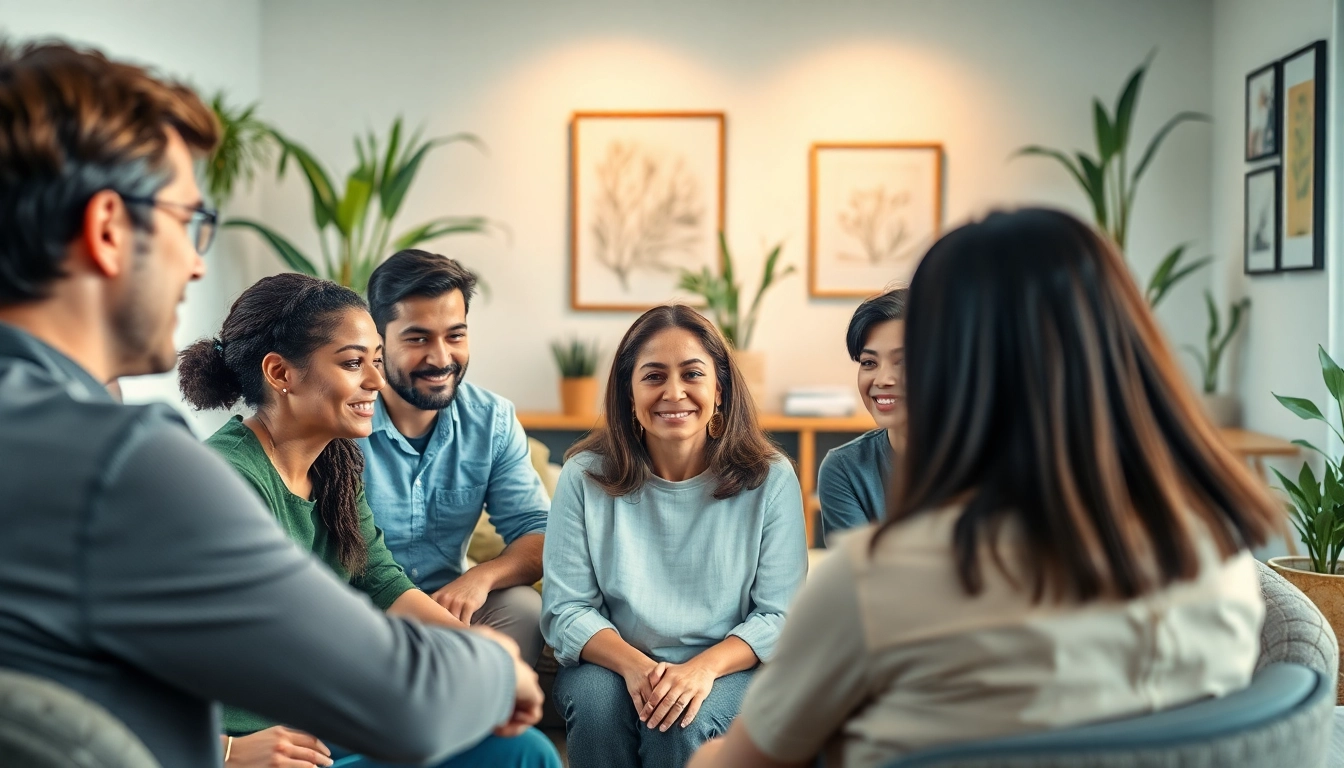
Building a Supportive Community
Having a solid support network is crucial for mental health. Building community can involve:
- Engaging in Social Activities: Joining clubs or community service initiatives can foster connections with others.
- Building Relationships: Taking the time to nurture friendships and connections provides crucial emotional support.
- Family Bonds: Maintaining open lines of communication with family members allows for shared experiences and mutual support.
The Future of Mental Health Awareness
Emerging Trends in Mental Health Treatment
The future of mental health treatment lies in both innovation and accessibility. Emerging trends include:
- Teletherapy: Remote therapy services have become increasingly popular, providing convenient access to mental health resources.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: Advances in understanding mental health conditions are leading to more individualized treatment approaches.
- Holistic Approaches: Integrating traditional mental health treatments with alternative therapies, such as acupuncture or nutrition, may improve outcomes.
The Role of Technology in Mental Health
Technology is transforming mental health services. Developments include:
- Mental Health Apps: Platforms offering mindfulness practices, self-help resources, and cognitive behavioral techniques are readily available.
- Online Peer Support Groups: Virtual communities allow individuals to share experiences and coping strategies.
- AI in Therapy: Artificial intelligence is being explored for its potential in providing preliminary support and resources.
Advocacy and Education for Better Mental Health
Increasing mental health awareness through education and advocacy is key to dismantling stigma. Efforts include:
- Workplace Programs: Implementing mental health initiatives in workplaces encourages a supportive culture.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Educating the public about mental health through campaigns can foster understanding and compassion.
- School-Based Initiatives: Incorporating mental health education in schools equips younger generations with knowledge and coping skills.














Leave a Reply